
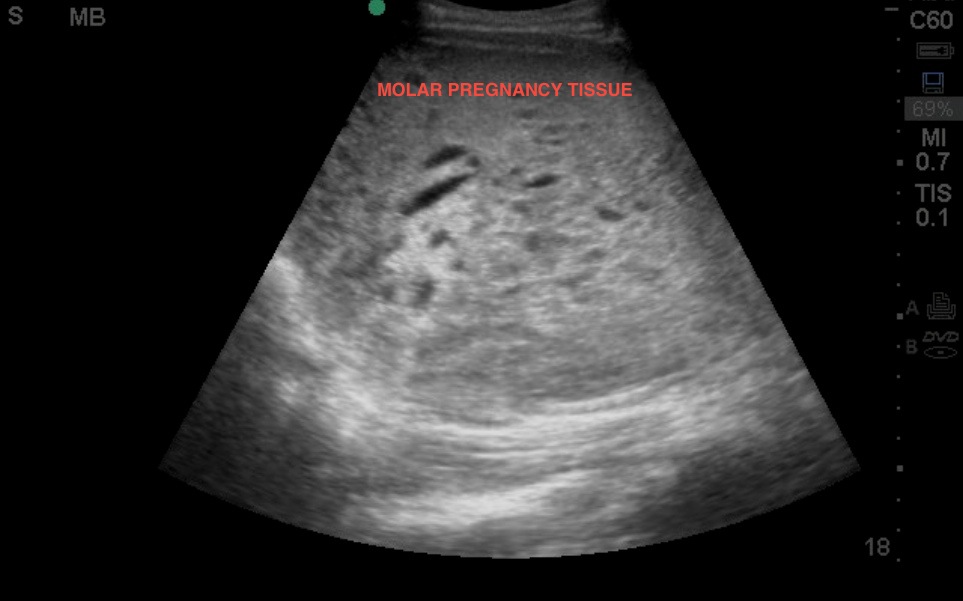
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Hydatidiform Mole. Powell M, Buckley J, Worthington B, Symonds E. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: A Spectrum of Radiologic Diagnosis. Images in Radiology: Complete Hydatidiform Mole with Live Pregnancy in a Twin Gestation. Sonographic Diagnosis of Partial Hydatidiform Mole. Takes place when an egg is fertilized by two sperms, which makes the embryo to. Fine C, Bundy A, Berkowitz R, Boswell S, Berezin A, Doubilet P. PARTIAL MOLAR PREGNANCY: Abnormal placenta tissue with embryo tissue can be seen. Please refer to the dedicated articles for discussion on the radiographic features:Ī complete mole can progress to invasive mole (~15%) or to gestational choriocarcinoma (~7%). In the classic case of molar pregnancy, quantitative analysis of beta-HCG shows hormone levels in both blood and urine greatly exceeding those produced in normal pregnancy at the same stage. The chorionic villi are converted into a mass of clear vesicles that resemble a cluster of grapes. LocationĬomplete hydatidiform moles usually occupy the uterine cavity and are rarely located in fallopian tubes or ovaries. The hydatidiform mole itself is one of a group of rare conditions called gestational.
With partial moles, the karyotype is usually triploid (69XXY), the result of fertilization of a normal egg by two sperm, one bearing a 23X chromosomal pattern and the other a 23Y chromosomal pattern. Thats why molar pregnancy is sometimes called. All the chromosomes are derived from a single sperm in 90% or less likely two sperms, suggesting fertilization of a single egg that has lost its chromosomes.

Ninety percent of complete hydatidiform moles have a 46XX diploid chromosomal pattern.
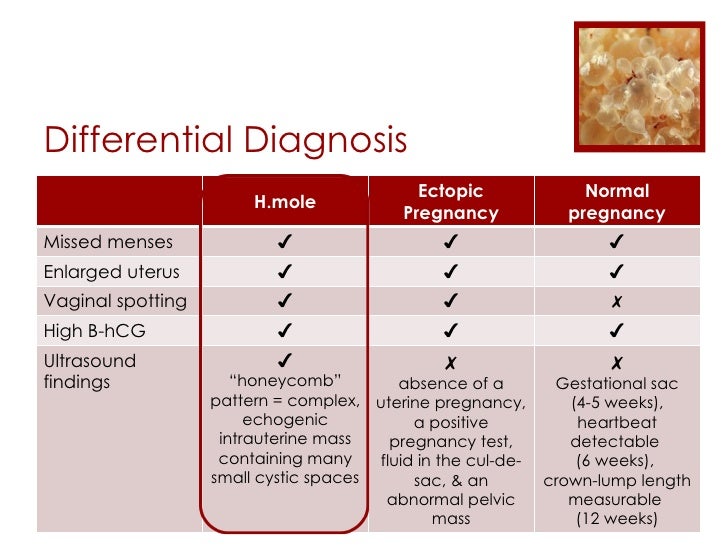
Rarely, moles co-exist with a normal pregnancy ( co-existent molar pregnancy), in which a normal fetus and placenta are seen separate from the molar gestation. partial moles usually occur with an abnormal fetus or may even be associated with fetal demise.complete moles are associated with the absence of a fetus.Pathology SubtypesĪ hydatidiform mole can either be complete or partial. The absence or presence of a fetus or embryo is used to distinguish the complete from partial moles: There is a relatively increased prevalence in Asia (for example compared with Europe). Molar pregnancies are one of the common complications of gestation, estimated to occur in one of every 1000-2000 pregnancies 3. These moles can occur in a pregnant woman of any age, but the rate of occurrence is higher in pregnant women in their teens or between the ages of 40-50 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
